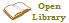Compact disc
![The readable surface of a compact disc includes a spiral track wound tightly enough to cause light to [[diffraction grating|diffract]] into a full [[visible spectrum]].](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e8/CD_autolev_crop_new.jpg) The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was codeveloped by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. It uses the Compact Disc Digital Audio format which typically provides 74 minutes of audio on a disc. In later years, the compact disc was adapted for nonaudio computer data storage purposes as CD-ROM and its derivatives. First released in Japan in October 1982, the CD was the second optical disc technology to be invented, after the much larger LaserDisc (LD). By 2007, 200 billion CDs (including audio CDs, CD-ROMs and CD-Rs) had been sold worldwide.
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was codeveloped by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. It uses the Compact Disc Digital Audio format which typically provides 74 minutes of audio on a disc. In later years, the compact disc was adapted for nonaudio computer data storage purposes as CD-ROM and its derivatives. First released in Japan in October 1982, the CD was the second optical disc technology to be invented, after the much larger LaserDisc (LD). By 2007, 200 billion CDs (including audio CDs, CD-ROMs and CD-Rs) had been sold worldwide.Standard CDs have a diameter of , and are designed to hold up to 74 minutes of uncompressed stereo digital audio or about of data. Capacity is routinely extended to 80 minutes and by arranging data more closely on the same-sized disc. The Mini CD has various diameters ranging from ; they have been used for CD singles or delivering device drivers.
The CD gained rapid popularity in the 1990s, quickly outselling all other audio formats in the United States by 1991, ending the market dominance of the phonograph record and the cassette tape. By 2000, the CD accounted for 92.3% of the entire market share in regard to US music sales. The CD is considered the last dominant audio format of the album era, as the rise of MP3, iTunes, cellular ringtones, and other downloadable music formats in the mid-2000s ended the decade-long dominance of the CD.
The ''Digital Audio'' format was later adapted (as CD-ROM) for general purpose data storage and initially could hold much more data than a personal computer hard disk drive. Several other formats were further derived, both pre-pressed and blank user writable, including write-once audio and data storage (CD-R), rewritable media (CD-RW), Video CD (VCD), Super Video CD (SVCD), Photo CD, Picture CD, Compact Disc-Interactive (CD-i), Enhanced Music CD, and Super Audio CD (SACD) which may have a CD-DA layer. Provided by Wikipedia
-
901
-
902by Almeida e Araujo Correa de Lacerda, Jose MariaLocation: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1855
Book -
903
-
904Monumenta Ignatiana. Series secunda. Exercitia spiritualia S. Ignatii de Loyola et eorum directoria.by Ignatius, of Loyola, Saint, 1491-1556Location: Dinand Library, College of the Holy Cross
Created 1955
Book -
905
-
906
-
907
-
908
-
909
-
910
-
911
-
912
-
913
-
914
-
915
-
916
-
917
-
918
-
919
-
920
-
921
-
922
-
923
-
924
-
925by Pinamonti, Giovanni Pietro, 1632-1703Location: Cudahy Archives, Loyola University Chicago
Created 1798
Book -
926
-
927
-
928by John Chrysostom, Saint, -407Location: Cudahy Archives, Loyola University Chicago
Created 1702
Book -
929
-
930
-
931
-
932by Vaughan, Herbert, 1832-1903, Dowling, Cornelius, Noonan, James, Vaughan, John S. (John Stephen), 1853-1925, Vaughan, Bernard, 1847-1922Location: Lauinger Memorial Library, Georgetown University
Created 2013
CONNECT TO ONLINE RESOURCE.
Kit -
933
-
934
-
935
-
936
-
937
-
938
-
939
-
940
-
941
-
942
-
943