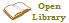Compact disc
![The readable surface of a compact disc includes a spiral track wound tightly enough to cause light to [[diffraction grating|diffract]] into a full [[visible spectrum]].](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e8/CD_autolev_crop_new.jpg) The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was codeveloped by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. It uses the Compact Disc Digital Audio format which typically provides 74 minutes of audio on a disc. In later years, the compact disc was adapted for nonaudio computer data storage purposes as CD-ROM and its derivatives. First released in Japan in October 1982, the CD was the second optical disc technology to be invented, after the much larger LaserDisc (LD). By 2007, 200 billion CDs (including audio CDs, CD-ROMs and CD-Rs) had been sold worldwide.
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was codeveloped by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. It uses the Compact Disc Digital Audio format which typically provides 74 minutes of audio on a disc. In later years, the compact disc was adapted for nonaudio computer data storage purposes as CD-ROM and its derivatives. First released in Japan in October 1982, the CD was the second optical disc technology to be invented, after the much larger LaserDisc (LD). By 2007, 200 billion CDs (including audio CDs, CD-ROMs and CD-Rs) had been sold worldwide.Standard CDs have a diameter of , and are designed to hold up to 74 minutes of uncompressed stereo digital audio or about of data. Capacity is routinely extended to 80 minutes and by arranging data more closely on the same-sized disc. The Mini CD has various diameters ranging from ; they have been used for CD singles or delivering device drivers.
The CD gained rapid popularity in the 1990s, quickly outselling all other audio formats in the United States by 1991, ending the market dominance of the phonograph record and the cassette tape. By 2000, the CD accounted for 92.3% of the entire market share in regard to US music sales. The CD is considered the last dominant audio format of the album era, as the rise of MP3, iTunes, cellular ringtones, and other downloadable music formats in the mid-2000s ended the decade-long dominance of the CD.
The ''Digital Audio'' format was later adapted (as CD-ROM) for general purpose data storage and initially could hold much more data than a personal computer hard disk drive. Several other formats were further derived, both pre-pressed and blank user writable, including write-once audio and data storage (CD-R), rewritable media (CD-RW), Video CD (VCD), Super Video CD (SVCD), Photo CD, Picture CD, Compact Disc-Interactive (CD-i), Enhanced Music CD, and Super Audio CD (SACD) which may have a CD-DA layer. Provided by Wikipedia
-
351by Kircher, Athanasius, 1602-1680Location: William H. Hannon Library, Loyola Marymount University
Created 1987
Book -
352by Chesterton, G. K. (Gilbert Keith), 1874-1936Location: University of St. Thomas Libraries, University of St. Thomas
Created 1916
Book -
353by Dauvillier, JeanLocation: University Libraries of CUA, Catholic University of America
Created 1936
Book -
354by Castillo, Carlos del, 1882-1957Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1928
Book -
355by Donnelly, Eleanor C. (Eleanor Cecilia), 1838-1917Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1898
Online Access
Online Access
Online Access
Electronic eBook -
356
-
357by D'Arcy, Martin Cyril, 1888-1976Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1928
Online Access
Online Access
eBook -
358
-
359
-
360by Döderlein, Johann Christoph, 1746-1792Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1790
Book -
361
-
362
-
363
-
364
-
365
-
366by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1671
Book -
367by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1671
Book -
368by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1673
Book -
369
-
370
-
371
-
372by Beaurepaire, Charles de, 1828-1908Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1892
Book -
373
-
374by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1676
Book -
375by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1666
Book -
376
-
377
-
378
-
379by Fonseca, Cristóbal de, 1550?-1621Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1629
Book -
380by Fonseca, Cristóbal de, 1550?-1621Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1598
Book -
381by Foyos, Christovam de, O.S.A., -1723Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1669
Book -
382
-
383
-
384by Hortolá, Cosme Damián, 1493- 1568Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1585
Book -
385
-
386
-
387by Ortega, Cristobal de, S.J., 1598-1686Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1671
Book -
388
-
389by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1758
Book -
390by Almeida, Christovam de, 1620-1679Location: Marian Library, University of Dayton
Created 1725
Book -
391by Corte, Corneille de, 1590?-1638Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1636
Book -
392by Nuño Cabezudo, Diego, ca. 1550-1614Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1601
Book -
393by Vert, Claude de, 1645-1708Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1710
Book -
394by Fonseca, Cristóbal de, d. 1621Location: Hesburgh Libraries, University of Notre Dame
Created 1603
Book -
395
-
396by Foucauld, Charles de, 1858-1916Location: Paul Bechtold Library, Catholic Theological Union
Created 1999
Book -
397by Délas, J. Cl (Jean-Claude)Location: Paul Bechtold Library, Catholic Theological Union
Created 1975
Book -
398by D'Arcy, Martin Cyril, 1888-1976Location: Paul Bechtold Library, Catholic Theological Union
Created 1991
Book -
399by Glandelet, Charles de, 1645-1725Location: Paul Bechtold Library, Catholic Theological Union
Created 1976
Book -
400by Doyle, Joseph C. (Joseph Cornell)Location: Paul Bechtold Library, Catholic Theological Union
Created 1983
Thesis Book